Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí
Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí Bảo Tồn. Bảo Vệ. Tận Hưởng.
 Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí
Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí  Mục lục
Mục lụcRừng cứng Piedmont
This ecological group contains a group of oak-hickory forests that occupy gentle to flat Piedmont uplands with impermeable clay subsoils. On high bedrock terraces of the Potomac Gorge in northern Virginia and occasionally elsewhere, flat-lying bedrock underlying shallow soil acts as a surrogate "hardpan" and supports similar vegetation. Piedmont Hardpan Forests occur from Virginia south to Georgia. Sites are usually underlain either by mafic rocks such as diabase or by acidic slates. Surficial soils are silt or clay loams, with an abrupt transition to heavy, plastic clay hardpans at depths of 23 to 38 cm (9 to 15 in). These shrink-swell clay soils pond water for brief or, at a few sites, prolonged periods during rainy weather, but tend to be very hard and dry during significant portions of the growing season. Post oak (Quercus stellata) is the most typical overstory tree, growing in nearly pure stands or in variable mixtures with pignut hickory (Carya glabra), Carolina shagbark hickory (Carya carolinae-septentrionalis, only in Charlotte, Halifax, and Pittsylvania counties), white oak (Quercus alba), blackjack oak (Quercus marilandica var. marilandica), Virginia pine (Pinus virginiana), and white ash (Fraxinus americana). Virginia pine increases following cutting and may dominate on heavily disturbed, clear-cut sites. Winged elm (Ulmus alata), sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua), and eastern red cedar (Juniperus virginiana) are characteristic understory trees. Shrubs include eastern redbud (Cercis canadensis var. canadensis), black haw (Viburnum prunifolium), fringetree (Chionanthus virginicus), and blueberries (Vaccinium spp.). In closed stands, there is often little herbaceous growth, while more open stands support large patches of xerophytic graminoids such as poverty oatgrass (Danthonia spicata), eastern needlegrass (Piptochaetium avenaceum), and little-headed nutrush (Scleria oligantha).
Các quần thể nằm trên các thềm suối cổ xưa, không bao giờ bị ngập lụt, nơi có các ao nước trong thời gian dài chứa hỗn hợp đặc biệt của các loài cây vùng cao và vùng đất ngập nước, nhưng tình trạng thủy văn của chúng đang có vấn đề và chúng được coi là cộng đồng của Hệ thống trên cạn. Trong các biến thể ẩm ướt theo chu kỳ này, các loài như cây sồi liễu (Quercus phellos), cây phong ngọt (Liquidambar styraciflua), cây nhựa ruồi rụng lá (Ilex decidua)), cây việt quất bụi rậm lông (Vaccinium fuscatum), cây ban Âu (Hypericum crux-andriae) và cây có mỏ (Rhynchospora spp.) xen kẽ với các loài chịu hạn được liệt kê ở trên.
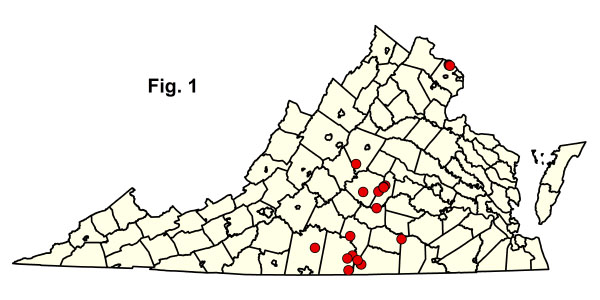
Rừng đất cứng Piedmont nằm rải rác khắp Piedmont trong môi trường đất đặc biệt và được coi là không phổ biến hoặc hiếm ở Virginia. Cây sồi cơ bản cứng phía Bắc - Rừng hồ đào (CEGL006216), hiện đang được xử lý trong Rừng hồ đào - Sồi cơ bản ECG, cũng có thể được đưa vào nhóm này, nhưng phát triển trên các giá thể có đặc điểm đất nền thay đổi đôi chút.
Tài liệu tham khảo: Fleming (2002a), Fleming (2007).
Nhấp vào đây để xem thêm ảnh về nhóm cộng đồng sinh thái này.
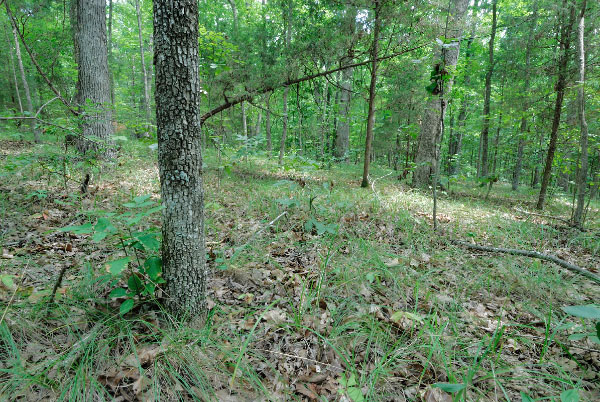 © DCR-DNH, Gary P. Fleming.
© DCR-DNH, Gary P. Fleming.
 Tải xuống bảng tính thống kê tóm tắt thành phần cho từng loại cộng đồng được liệt kê bên dưới.
Tải xuống bảng tính thống kê tóm tắt thành phần cho từng loại cộng đồng được liệt kê bên dưới.