Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí
Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí Bảo Tồn. Bảo Vệ. Tận Hưởng.
 Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí
Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí  Mục lục
Mục lụcRừng tuyết tùng trắng Đại Tây Dương than bùn
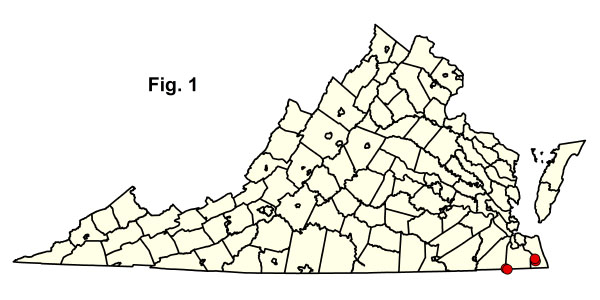
In Virginia, these coniferous forests are confined to saturated, oligotrophic, Coastal Plain peatlands. Peatland Atlantic White-Cedar Forests are endemic to terraces of the Embayed Region of extreme southeastern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina. Habitats are non-riverine wetland flats with deep organic soils (e.g., Great Dismal Swamp, Cities of Suffolk and Chesapeake) and remote peat flats beyond the range of wind-tidal flooding along the North Landing River (City of Virginia Beach). Atlantic white-cedar forests usually occupy relatively wet peatlands subject to infrequent catastrophic fires. Dense, even-aged stands become established when such fires remove most vegetation and debris, exposing suitable seedbeds. Throughout their maturation, these stands accumulate extensive dead wood and inflammable duff, making them increasingly susceptible to another stand-killing fire. Atlantic white-cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides) dominates the overstory, sometimes with red maple (Acer rubrum), swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora), or pines (Pinus serotina and Pinus taeda) as minor associates. Red bay (Persea palustris), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana), sweet pepperbush (Clethra alnifolia), big gallberry (Ilex coriacea), inkberry (Ilex glabra), shining fetterbush (Lyonia lucida), and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) are common small trees and shrubs. Cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum) and Virginia chain fern (Woodwardia virginica) are common herbs, while (Sphagnum spp.) and other mosses abundantly cover the ground.

Rừng tuyết tùng trắng Đại Tây Dương trên đất than bùn có đặc điểm thực vật tương tự như rừng thông ao và rừng Pocosin cũng như loại rừng hỗn giao thường xanh của rừng đầm lầy không ven sông. Chúng khác nhau ở sự thống trị của tán cây và mật độ cây bụi thấp hơn, cũng như mối liên hệ với các vùng đất than bùn rộng lớn trước đây thường xuyên xảy ra hỏa hoạn thảm khốc với khoảng thời gian lặp lại dài. Rừng tuyết tùng trắng Đại Tây Dương ở vùng đất than bùn rất hiếm trên toàn cầu và hiện nay chỉ còn lại một số ít tàn tích so với nơi phân bố trước đây của chúng do nạn khai thác gỗ và cháy rừng tràn lan. Do những xáo trộn này và việc đào mương rộng rãi, nhiều khu vực trước đây ở Đầm lầy Great Dismal đã được chuyển đổi thành Rừng đầm lầy không ven sông với sự thống trị của cây thích đỏ và cây tupelo đầm lầy. Cây tuyết tùng trắng Đại Tây Dương là vật chủ ấu trùng của loài bướm Hessel's Hairstreak (Mitoura hesseli) quý hiếm, được ghi nhận ở vùng đầm lầy Great Dismal.
Tài liệu tham khảo: Dabel và Day (1977), Day (1985), Dean (1969), Fleming và Moorhead (1998), Frost (1995), Stevens và Patterson (1998), Train và Day (1982).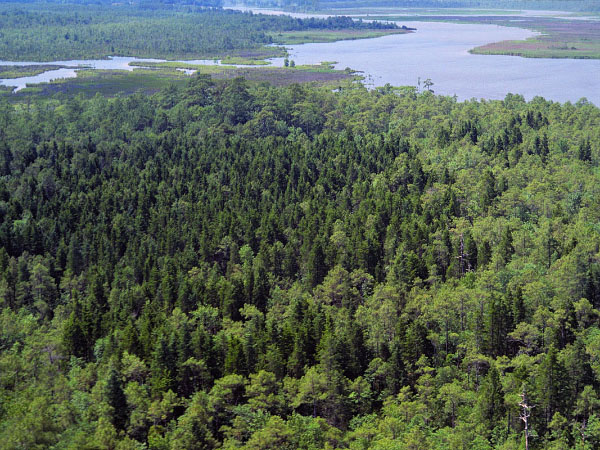 © DCR-DNH, Caren Caljouw.
© DCR-DNH, Caren Caljouw.
 Tải xuống bảng tính thống kê tóm tắt thành phần cho từng loại cộng đồng được liệt kê bên dưới.
Tải xuống bảng tính thống kê tóm tắt thành phần cho từng loại cộng đồng được liệt kê bên dưới.