Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí
Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí Bảo Tồn. Bảo Vệ. Tận Hưởng.
 Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí
Sở Bảo Tồn và Giải Trí  Mục lục
Mục lụcĐầm lầy ven biển
Nhóm này bao gồm tất cả các thảm thực vật gỗ ngập nước theo mùa, cũng như các khu rừng bão hòa, các vùng đất ngập nước ven biển được che chở và gần cửa sông. Ở môi trường sống ven biển, đặc điểm thảm thực vật của một loại thảm thực vật riêng lẻ có thể thay đổi rất nhiều tùy thuộc vào giai đoạn phát triển diễn thế và mức độ tiếp xúc với quá trình cắt tỉa của gió và hơi nước mặn. Kết quả là, cùng một loại thảm thực vật có thể được biểu hiện dưới dạng cây bụi, rừng hoặc rừng ở nhiều địa điểm khác nhau trong các điều kiện khác nhau. Một ví dụ điển hình là rừng đầm lầy ven biển loại liễu đen (Salix nigra), ban đầu có thể phát triển thành vùng cây bụi nhưng nhanh chóng đạt đến độ cao của rừng hoặc đất rừng khi cây trưởng thành. Tuy nhiên, nhóm này nhìn chung có thể được chia thành đầm lầy cây bụi ven biển và rừng đầm lầy ven biển, không chỉ theo đặc điểm sinh thái trưởng thành mà còn theo thành phần thực vật.
Đầm lầy cây bụi ven biển bị ngập theo mùa, thường là vùng đất cây bụi rậm rạp có các hốc đất phía sau cồn cát và các đầu cửa sông được che chắn, nơi nước mặt luôn hiện diện quanh năm. Mực nước ngầm cao và lũ lụt theo mùa hoặc không liên tục là đặc điểm của thủy văn. Cả nước ngầm và nước mặt thường là nước ngọt (< 0.5 ppt), mặc dù nước mặn có thể đọng lại ở những khu vực này sau những đợt bão dâng cao đột ngột trong các sự kiện như bão. Đất được phân tầng, với lớp bùn mỏng dày tới 30 cm (12 in) trên cát ướt. Thành phần loài của những cộng đồng này rất đa dạng và thay đổi đôi chút từ bờ biển đông nam (Thành phố Virginia Beach) đến bờ biển phía Đông (Quận Accomack và Northampton). Trong toàn vùng, cây sim (Morella cerifera) là đặc điểm chiếm ưu thế. Các khu vực phía Nam đặc trưng có cây inkberry (Ilex glabra) và cây việt quất bụi cao (Vaccinium spp.). Những loài này ít quan trọng hơn trong nhóm này ở phía bắc Bờ biển phía Đông. Dây leo của cây thường xuân độc (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) thường đan xen với các cây bụi ở hầu hết các vùng đầm lầy này. Các lớp thảo mộc có thể giàu dương xỉ, bao gồm cả dương xỉ hoàng gia (Osmunda spectabilis), dương xỉ đầm lầy (Thelypteris palustris var. pubescens), dương xỉ xích lưới (Lorinseria areolata) và dương xỉ xích Virginia (Woodwardia virginica), nhưng cũng bao gồm nhiều loại cây thân thảo như cây cỏ đồng tiền đầm lầy xoắn (Hydrocotyle verticillata). Phân loại, phân bố địa lý và tình trạng bảo tồn của các đầm lầy cây bụi ven biển hiện vẫn chưa chắc chắn và cần được nghiên cứu chuyên sâu.
Maritime swamp forests are seasonally flooded and saturated forests occupying large, protected, interdune swales, flats immediately behind tidal marshes, and the bottoms of streams just inland from estuarine zones. These communities definitely occur from southern New Jersey to North Carolina, but may range further south. In Virginia, stands are scattered along the outer Coastal Plain from the Eastern Shore (Accomack and Northampton Counties) to Cape Henry and False Cape (City of Virginia Beach). The status of these communities on the western shore of the Chesapeake Bay is less clear. Habitats are generally characterized by hummock-and-hollow microtopography, with mucky to sandy, mottled soils and sizeable areas of seasonally standing water. The apparent nutrient status and flooding regimes of soils are highly variable and probably relate to the wide compositional variation in documented stands. Dominant overstory trees in the seasonally flooded forests of the group include red maple (Acer rubrum), sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua), swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora), blackgum (Nyssa sylvatica), black willow (Salix nigra), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana) and, less frequently, bald cypress (Taxodium distichum) and Atlantic white-cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides). Shrubs are diverse but usually include highbush blueberries (Vaccinium fuscatum and/or Vaccinium formosum), wax myrtle (Morella cerifera), red bay (Persea palustris), and greenbriers (Smilax spp.). Herb layers range from floristically depauperate, with dominance by Virginia chain fern (Woodwardia virginica) or low shrubs, to species-rich with a diversity of marsh and swamp species.
Saturated pine forests in this group occur in back-dune depressions of barrier islands and on terrace flats bordering estuaries further inland. In Virginia, these communities are locally scattered along the Chesapeake Bay (both shores) and its major estuarine tributaries, as well as around Back Bay and estuarine tributaries of Currituck Sound in the southeastern corner of the state. Occasionally, stands occupy slightly elevated "islands" within the upper portions of salt marshes. Habitats are level flats with shallow water tables and hummock-and-hollow microtopography. Areas of seasonally ponded water and organic muck are present; elsewhere, soils are heavily mottled sands. Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) is the usual dominant overstory tree, sometimes with hardwood associates. Wax myrtle (Morella cerifera) and vines of common greenbrier (Smilax rotundifolia) and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) are usually abundant. In southern areas (e.g., on False Cape), pond pine (Pinus serotina) and inkberry (Ilex glabra) are characteristic woody associates. Wetland species such as cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum), royal fern (Osmunda spectabilis), switchgrass (Panicum virgatum var. virgatum and var. cubense), and smartweeds (Persicaria spp.) dominate species-poor herb layers. A distinctive variant occurring in southeastern Virginia and North Carolina has a dense understory of switch cane (Arundinaria tecta). Some of the maritime wet pine forests appear to represent formerly open, bog-like maritime grasslands that have been invaded by loblolly pines. There is a well documented example of this variant from the Eastern Shore (Assateague Island, Accomack County) and at least one poorly documented occurrence on False Cape (City of Virginia Beach). These stands occupy swales in sheltered back dunes that are protected from salt spray except during major storm surges. A thin organic layer, frequently covered by dense mats of Sphagnum mosses, is usually present at the soil surface. On Assateague Island the vegetation is an open stand of young, salt-spray-stunted loblolly pine, with a very sparse shrub layer. Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) forms dense mats locally beneath the pines. Elsewhere, scattered herbs include saltmeadow cordgrass (Spartina patens), tall flat panic grass (Coleataenia rigidula ssp. rigidula), and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum var. virgatum) in shallow pools and depressions, and bushy bluestem (Andropogon glomeratus), Virginia marsh St. John's-wort (Triadenum virginicum), beaksedges (Rhynchospora spp.), twisted yellow-eyed grass (Xyris torta), white-bracted thoroughwort (Eupatorium leucolepis), and water sundew (Drosera intermedia) in wet sand and Sphagnum mats. Maritime Wet Pine Forests are similar to and often intergrade with non-wetland maritime loblolly pine forests and maritime evergreen forests.
Động lực sinh thái của đầm lầy biển, cũng như sự khác biệt của chúng với rừng đầm lầy nội địa, vẫn chưa được hiểu rõ. Giống như các cộng đồng khác trong vùng biển, họ có khả năng bị ảnh hưởng bởi bão, hơi muối và cồn cát di chuyển. Rừng đầm lầy ven biển không phổ biến hoặc hiếm ở Virginia và đang bị xâm lấn bởi hoạt động phát triển, khai thác gỗ và ô nhiễm nông nghiệp.
Tài liệu tham khảo: Harvill (1967), Fleming và Moorhead (1998), The Nature Conservancy (1997).
Nhấp vào đây để xem thêm ảnh về nhóm cộng đồng sinh thái này.
 © DCR-DNH, Gary P. Fleming.
© DCR-DNH, Gary P. Fleming.
CÁC LOẠI CỘNG ĐỒNG ĐẠI DIỆN:
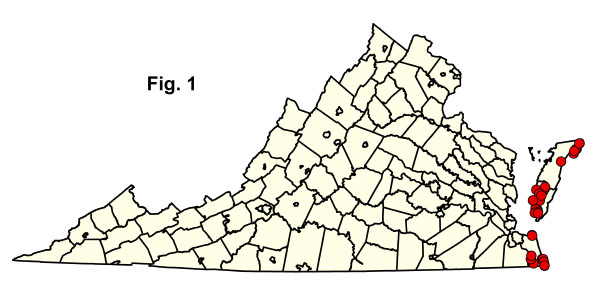
Dữ liệu đã được thu thập từ 33 lô đất ngập nước ven biển nằm ở ba quận đồng bằng ven biển bên ngoài (Hình 1). Hầu hết các mẫu này là từ đầm lầy có rừng và cần có thêm dữ liệu từ đầm lầy cây bụi. Phân tích dữ liệu thảm thực vật biển Virginia, mặc dù có phần hạn chế, dường như đủ để mô tả thành phần các loại thảm thực vật biển Virginia và mối quan hệ của chúng với USNVC. Việc ghi chép lại các cộng đồng trong nhóm này từ bờ biển phía tây của Vịnh Chesapeake vẫn là ưu tiên hàng đầu. Nhấp vào bất kỳ mã CEGL nào được tô sáng bên dưới để xem mô tả USNVC toàn cầu do NatureServe Explorer cung cấp.
 Tải xuống bảng tính thống kê tóm tắt thành phần cho từng loại cộng đồng được liệt kê bên dưới.
Tải xuống bảng tính thống kê tóm tắt thành phần cho từng loại cộng đồng được liệt kê bên dưới.